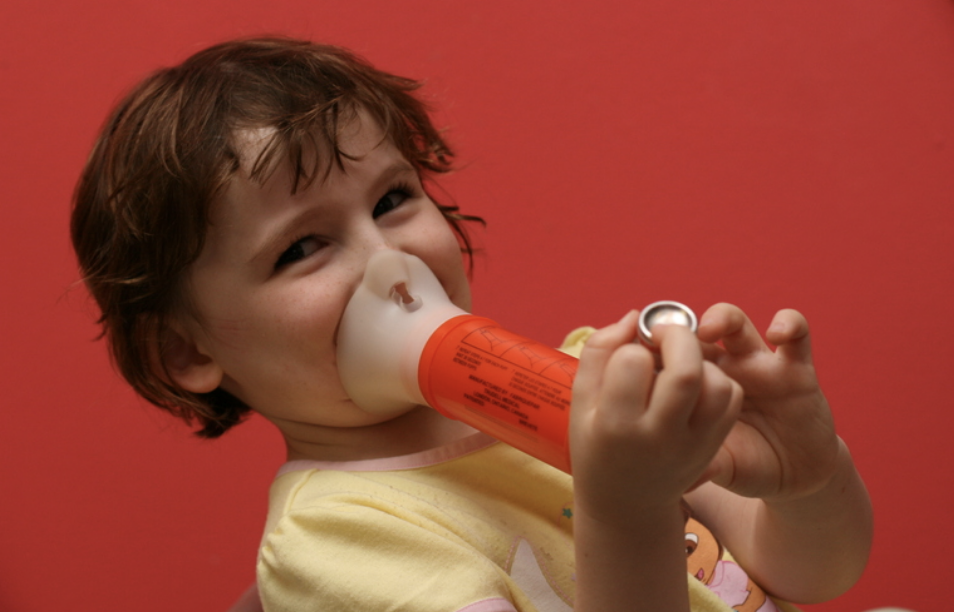

Asthma is a common medical condition found in the majority of people. It is quite common for the general public. However, what they do not know is that there is some link between sleep-disordered breathing in asthma patients. Asthma patients commonly suffer from obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, a well-known form of sleep apnea. This is because the common factor between these two condition is respiratory complications. Due to this reason, there is growing evidence suggesting a significant connection between the two.
Typically, asthmatic patients should look out for obstructive sleep apnea risk factors. If you are someone suffering from one or both of these conditions, then you must stick to the end. This article explores the intricate relationship between sleep apnea and asthmatic patients, shedding light on how these conditions intersect and impact each other.
There is a bidirectional relationship between bronchial Asthma and Obstructive sleep apnea. To understand it deeply, you need to first understand these conditions individually:
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that causes a pause in breathing (apneas) while sleeping. The severity of apneas depends on various factors, such as the degree of airway blockage and the brain's functioning. There are three main types: obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome, also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea. Middle-aged or obese people are at a higher risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
The main cause of this condition is the excessive relaxation of throat muscles, leading to a partial or complete blockage of the airway. This could be treated through Continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea may experience excessive daytime sleepiness, loud snoring and difficulties in concentration.
All these factors, especially the episodes of apnea, lead to asthma exacerbation. Apart from this, sleep apnea can contribute to various other health problems, such as hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
Severe Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Common symptoms of Asthma include wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may vary over time.
Asthma is typically triggered by allergens, irritants, or infections that cause the airways to become inflamed and constricted. It can be managed with medications and lifestyle modifications, but poorly controlled Asthma can lead to significant respiratory distress and reduced quality of life.
Research has increasingly revealed a bidirectional relationship between sleep apnea and Asthma. This means that not only can Asthma worsen the severity of sleep apnea, but sleep apnea can also exacerbate asthma symptoms.
Asthma can cause severe sleep apnea because it is mainly related to difficulty in breathing. The main factor includes Airway Inflammation, in which chronic inflammation associated with Asthma can lead to increased airway resistance, making it more likely for the airway to collapse during sleep.
Some severe asthma exacerbations are caused by sleep apnea. The driving factors include the triggering of airway inflammation due to repeated exposure to apneas, reduction in medication effectiveness for Asthma, and increase in allergic response in people with allergic Asthma.
It is important to understand the connection between Asthma and sleep apnea to effectively manage both conditions. Let us look at some strategies to do so :
It is important for patients with both Asthma and sleep apnea to receive properly coordinated care from a team of healthcare professionals, including pulmonologists, allergists, and sleep specialists, to make sure that both of them get properly addressed and do not conflict with the treatment plans.
Proper management of Asthma becomes even more crucial when it coexists with sleep apnea. Manage it with proper medication and a healthy routine or lifestyle modification to make sure it does not worsen sleep apnea.
Treatment involving lifestyle modification, therapy, and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices depending on the level of sleep apnea is essential to treat sleep apnea to improve sleep quality and reduce the impact on Asthma.
Obesity is a common risk factor for both conditions. Having a proper diet and including regular exercise in your daily life will help you to lose weight, which can significantly improve symptoms of both Asthma and sleep apnea and further reduce the need for medications and other interventions.
Allergies can trigger both Asthma and sleep apnea symptoms; thus, it is important to identify and manage the allergens with the help of an allergist. They will give you some strategies, such as allergen avoidance, immunotherapy, and antihistamines, which can help you control your condition.
Healthy sleep habits can benefit patients with both conditions. Maintaining a good sleep schedule by creating a comfortable and peaceful sleep environment while avoiding stimulants that can make you active close to bedtime can enhance sleep quality and lead you to a healthy lifestyle.
Positional therapy can be effective for sleep apnea in some cases. Strategies like changing sleeping positions to reduce airway obstruction during sleep use specialized pillows and devices that encourage sleeping in positions that minimize apnea events are involved in this therapy.
CPAP or other PAP devices are commonly used to treat sleep apnea. Proper mask fit and adjustment of pressure are important in this therapy, which involves CPAP and PAP machines that allow a continuous stream of air pressure to keep the airway open so the patient can have a proper and no disturbance sleep.
The relationship between Asthma and sleep apnea is complex yet important to understand because each condition potentially makes the other worse. A proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to effectively manage both conditions. Patients suffering from either of these conditions or both should look for healthcare professionals to monitor their condition well and manage it accordingly by making lifestyle changes that can improve their sleep quality. Doing so can improve their quality of life so that they can enjoy better respiratory health and live a healthy lifestyle.
Leave a comment